
Also, changing the metal mobility via immobilization or mobilization with soil amendments and green remediation has been recognized as a calm remediation tactic. However, such remedial methods are not economically viable, destructive to the agro-ecosystems, impractical for large quantities of hazardous waste.

For cleaning-up of HM contamination, various practices and technologies such as adsorption, oxidation, reduction, precipitation, ion-exchange, coagulation-flocculation, electrochemical methods, leaching/acid extraction, and soil washing have been adopted. Their accumulation in agricultural soils could potentially increase the risk of entry into the food/feed chain, threatening human and animal health.
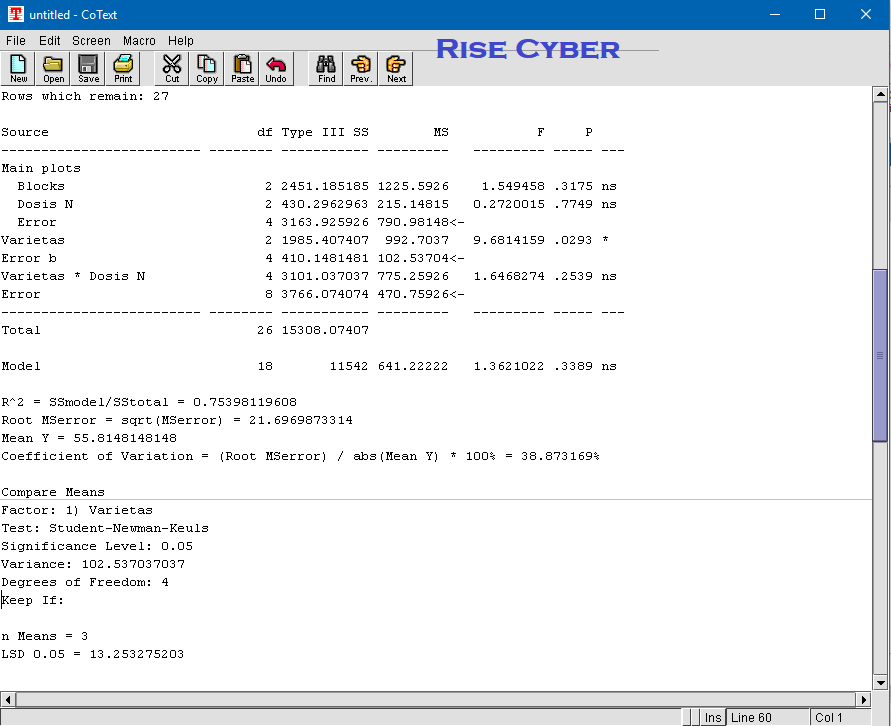
tricolor under field conditions could be recommended for future directions to confirm the results.Ĭontaminated soils by heavy metals (HMs) are the global environmental problem caused by certain natural processors, including erosion, mineral weathering, volcano eruptions and anthropogenic activities such as industrialization, urbanization, agricultural practices (application of HMs-containing pesticides and fertilizers, sewage sludge, etc.) and casting minerals. Additionally, long-term application of organic mobilization amendments and continued growth of A. tricolor as a successful ornamental candidate that, along with organic mobilization amendments, most efficiently develop soil health, reduce metal toxicity, and recommend remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils. El-Madabeg soil treated with vinasse sugarcane gave the highest RF values 6.40, 3.26, and 4.02% for Pb, Zn, and Cu, respectively, than the control. In all studied soils, the application of organic materials increased the remediation factor (RF) than the control. Also, an increase in Zn concentration due to EDTA application was 58, 42, and 56% for Helwan, El-Gabal El-Asfar, and El-Madabeg soil, respectively. HA application caused the highest uptake as shown in Pb concentration by more than 5 times in Helwan soil and EDTA by 65% in El-Gabal El-Asfar soil while VSC increased it by 110% in El-Madabeg soil.

The uptake of Pb and Zn significantly ( p > 0.05) increased due to applying all organic materials to the studied soils. tricolor plant compared to the control treatment. Our results revealed all organic materials in all studied soils, except EDTA in EL-Gabal El-Asfar soil, significantly increased the dry weight of the A. The studied soils collected from Helwan, El-Gabal El-Asfar (Cairo Governorate), Arab El-Madabeg (Assiut Governorate), Egypt, and study have been conducted under pot condition. The study aimed to enhance the uptake of HMs (Pb, Zn, and Cu) via amending poultry litter extract (PLE), vinasse sugarcane (VSC), and humic acid (HA) as natural mobilized organic materials compared to ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA), as a common mobilized chemical agent by A. tricolor plant in metal phytoremediation from the polluted sites. Site-specific detailed information is not available on the use of A. has attractive characteristics acquiring a higher growth rate and large biomass when grown at heavy metal contaminated soils. Accumulation of heavy metals (HMs) by ornamental plants (OPs) from contaminated agriculture soils is a unique technique that can efficiently reduce the metal load in the food chain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
